In recent years, the market of 10,000-watt trend has continued to rise and quickly swept the laser industry. With the popularization of 20kW and 30kW high-power laser cutting machines, users have gradually tasted the sweetness brought by the power increase, both in terms of processing capacity and efficiency.
And the road to industrial processing of 10,000 watts will not stop here. Then 2023 became the starting point for the industrial application of 60,000-watt fiber lasers. Such a fast pace will inevitably attract many doubts. Unexpectedly, in less than half a year, 60,000-watt fiber laser cutting machines were in short supply. The steel structure industry has repeatedly purchased ultra-high-power laser cutting to replace plasma cutting, and all signs seem to be very different from the doubts. From the perspective of traditional process replacement and application scenarios, the significance of ultra-high-power lasers for metal cutting processing is extraordinary.
The market process of laser replacing plasma is accelerating
Long before the popularization of laser cutting, plasma cutting was the most mature process in the field of metal processing. It uses the heat of high-temperature plasma arc to partially melt the metal at the incision of the workpiece, and uses the momentum of high-speed plasma to remove the molten metal to form an incision. Its processing quality and cost are relatively considerable. At this time, plasma cutting is still widely used in the field of medium and thin plates due to its advantages such as fast cutting speed and smooth end face.
However, with the rise of lasers, laser cutting began to have a certain degree of impact on plasma cutting. In the field of thin plate cutting, kilowatt-class fiber lasers have absolute advantages over plasma cutting quality and efficiency. High precision, small slits, small heat-affected zones, no burrs on the edges and fast cutting speeds make them the first choice in this field. In contrast, the disadvantages of plasma cutting have become prominent.
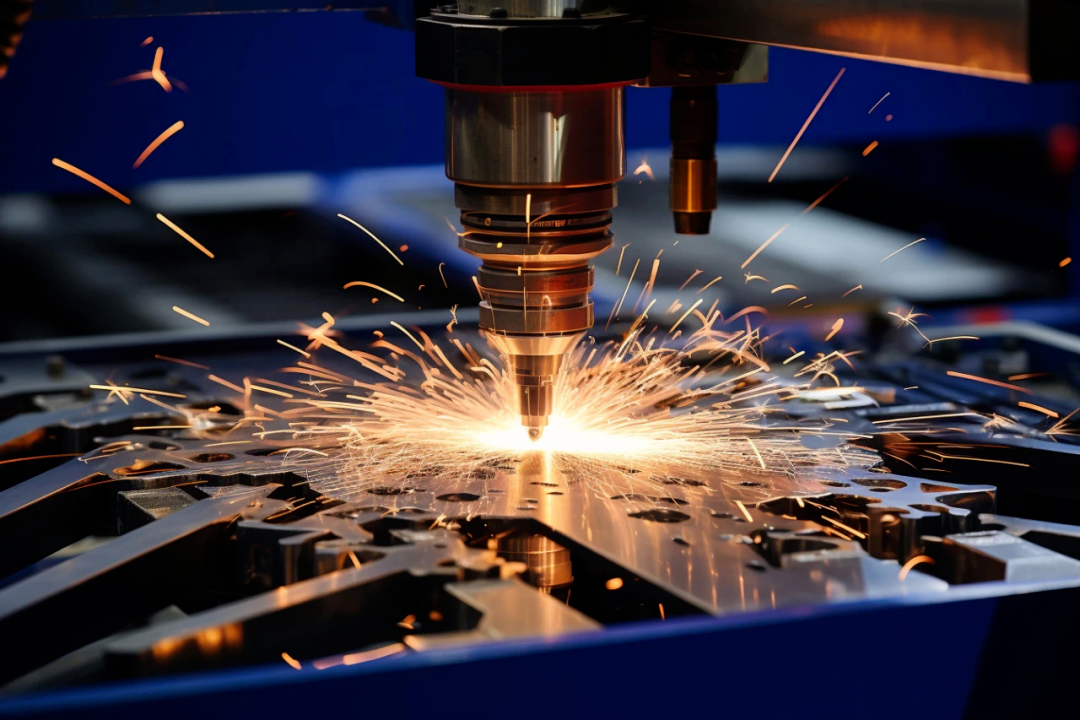

Laser cutting has gradually won market recognition with higher speed, higher precision and more environmental protection. In the early days when the laser power was low, laser cutting only had advantages in thin plate processing and could not process medium and thick plates. In recent years, the power of lasers has continued to rise, from 6kW to 8kW, 12kW, 15kW, 20kW, and then to 30kW. The power has been continuously improved, the process has been continuously improved, and the bottleneck of laser cutting has been continuously broken.
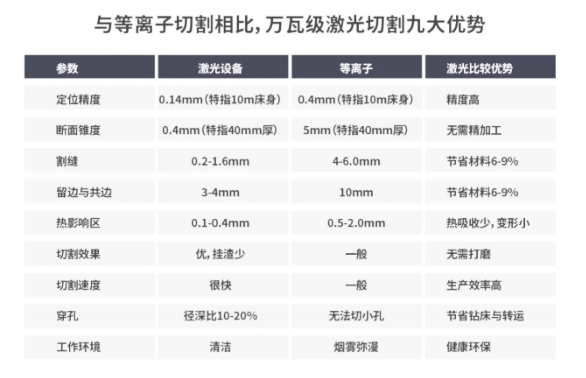
Until 2020, the emergence of 10,000-watt laser cutting technology has brought new vitality to metal processing and promoted the transformation and upgrading of traditional industries. Since then, laser cutting has entered the 10,000-watt era. At the same time, it has launched a second round of challenges to plasma cutting, which has had a strong impact on the huge plasma cutting market.
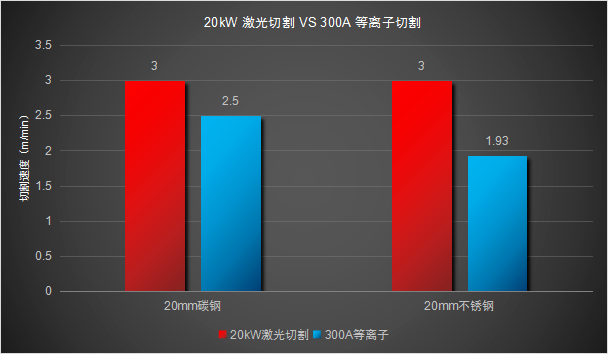
For carbon steel/stainless steel within 20mm, the efficiency of 20kw laser cutting exceeds that of 300A plasma, but the one-time purchase cost is far higher than that of plasma cutting. Users are still hovering between the two, and it is too early to talk about substitution.
In 2022, the popularity of 30kW lasers has truly shaken the dominant position of plasma cutting, and at the same time began to impact plasma cutting in the field of medium and thick plates.
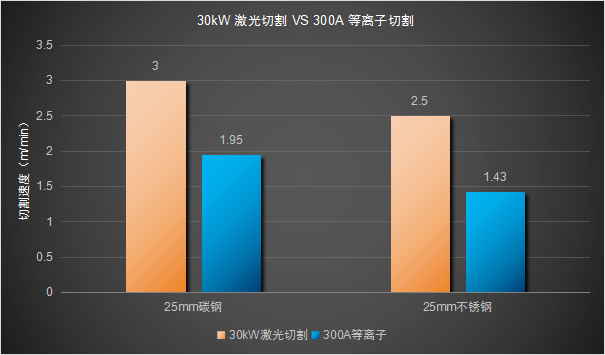
In 2023, domestic ultra-high power fiber laser technology has made rapid progress, and 60kW laser has emerged, truly breaking through the limitations of cutting thickness and once again challenging plasma cutting.
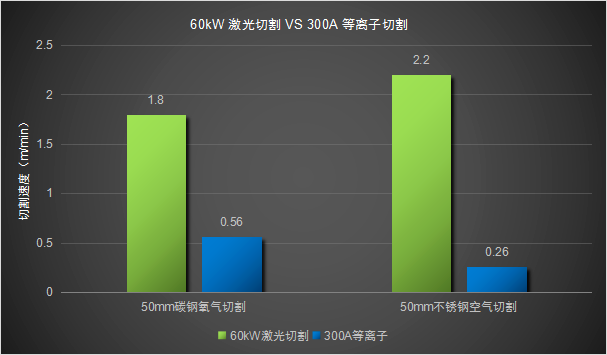
From the perspective of cutting efficiency and cutting quality, 60kW laser cutting has the ability to completely replace plasma cutting. At present, laser cutting and plasma cutting have formed a balance in terms of overall economic benefits, each occupying half of the market. Ultra-high power laser cutting shows a very broad application prospect and is expected to become a mainstream metal processing method in the future.
Application scenarios are expected to achieve "full replacement"
Before the popularization of 10,000-watt lasers, laser cutting was mainly better than plasma cutting in thin plates below 10mm, but in the 30-50mm range, plasma cutting has a significant speed advantage, and laser cutting cannot compare with it.
With the rise of 10,000-watt lasers, and now the widespread popularization of 60kW, laser cutting is expanding its coverage to the field of medium and thick plate cutting. At this time, the plasma cutting market has shrunk sharply and has been gradually replaced in some application scenarios.
Behind the rapid rise in the market share of laser cutting, on the one hand, is the maturity of high-power fiber laser technology; on the other hand, it is due to the rapid development of manufacturing industries such as steel structure, shipbuilding, aerospace, nuclear power, etc., which has put forward an urgent demand for efficient and high-quality thick plate cutting.
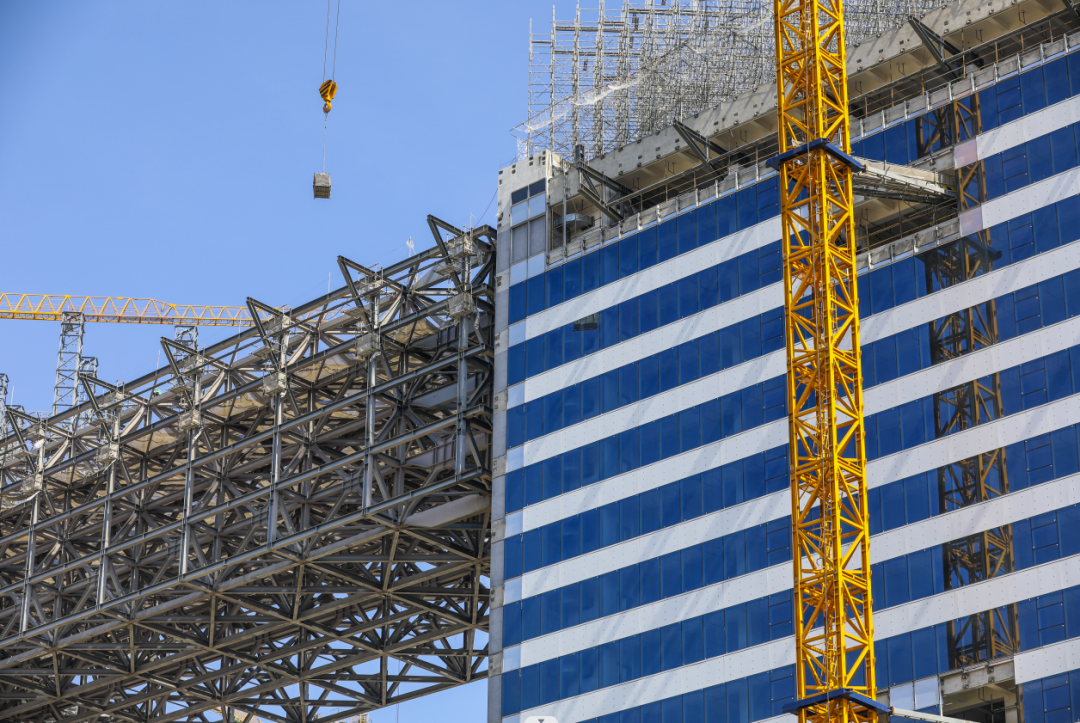

In the steel structure industry, carbon steel plays a vital role. It is widely used in structural support materials such as beams, columns and steel plates, as well as bridges, building skeletons and high-rise buildings. With the upgrading of the industry, the market has put forward new requirements for carbon steel processing, high-quality incisions, smooth edges, and reduced difficulty in subsequent processing; fast cutting speed, improved production efficiency; small heat-affected zone, reduced material deformation and cracking. For the steel structure industry, ultra-high power laser cutting meets more demanding processing requirements. The advantages of high efficiency, high quality and low cost further help laser cutting replace plasma and become the mainstream technology of the industry in the future.
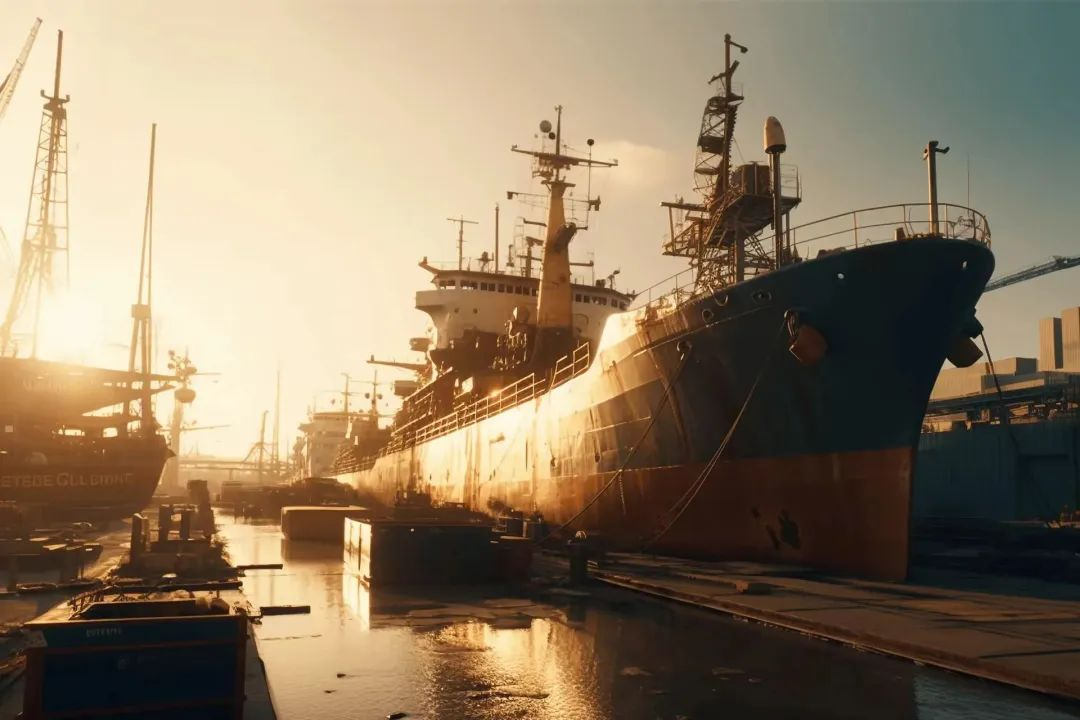

With the advancement of laser cutting technology, laser cutting machines have been widely used in the shipbuilding industry. This new cutting technology is replacing traditional methods such as stamping, shearing, and plasma cutting, and has already occupied a dominant position in the field of sheet metal processing in shipbuilding.
Laser cutting technology enables the shipbuilding industry to achieve efficient and high-precision metal processing, short production cycles and low production costs. While ensuring the quality of the equipment, it helps to reduce the installation workload, shorten the installation cycle, and save materials and labor costs.
As a non-contact, non-polluting, low-noise, and material-saving green processing technology, laser cutting technology has begun to show its digital, intelligent, and flexible characteristics. As my country's independently developed high-power lasers enter the large-scale installation stage, the prices of imported laser products have begun to gradually decrease. The application scope of laser processing in the shipbuilding industry has gradually expanded, and the large-scale popularization of laser cutting and welding skills in ship occupations is just around the corner.
Outlook - The future of fiber lasers
Although the editor recognizes the importance of high-power lasers, power increase is still one of the reasons for the industry's internal volume. While paying attention to the comprehensive performance of lasers and the upgrading of underlying technologies, we should also continue to explore application potential, such as medium and thick plate laser welding technology. From a market perspective, China is the largest country in infrastructure. In the future, the further development of fiber lasers will also allow China to move from a "manufacturing power" to a "manufacturing power." There is no doubt that China's laser industry has been moving forward at a fast pace and will soon usher in the next "golden decade"!



